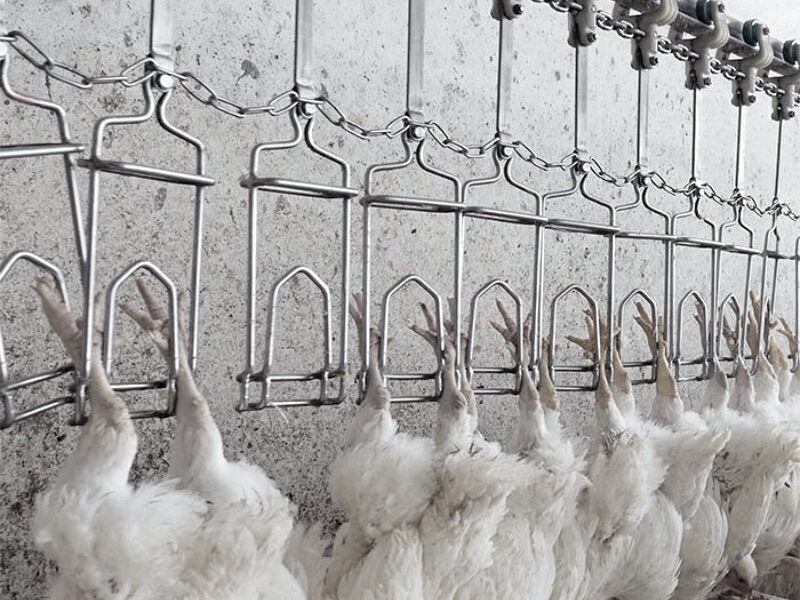
4.0 STUNNING AND SLAUGHTER
4.0.1 Stunning must render birds immediately insensible to pain on the first attempt.
4.0.2 Stunning must ensure birds remain insensible to pain until the bird dies due to slaughter or blood loss.
4.0.3 All birds must be rendered insensible to pain prior to being cut.
4.0.4 If any sign of sensibility is observed at any time after stunning, the bird must be re-stunned immediately.
4.0.5 Equipment used to shackle, stun, bleed and kill a bird must be kept and maintained in line with the manufacturer’s instructions.
4.0.6 Equipment used to shackle, stun, bleed and kill a bird must only be used within the design parameters described by the manufacturer.
4.0.7 For all stunning equipment there must either be a manual back-up or reserve equipment for use in case of emergency or breakdown; or there must be a protocol to shut down the line/stop slaughtering and remove any live birds from shackles or cones.
4.0.8 Staff that carry out stunning and bleeding must have been trained and be competent to use the available equipment.
4.1 Approved methods of stunning
The approved methods for rendering poultry insensible are:
4.2 Penetrating captive bolt and non-penetrating captive bolt.
4.3 Electric stunning via hand-held devices or dry plate.
4.4 Electric stunning via water bath.
4.5 Gas: Controlled Atmosphere Stunning (CAS) and Controlled Atmosphere Killing (CAK).
4.2 Use of a penetrating or non-penetrating captive bolt stunner
4.2.1 When using a captive bolt gun a type of sufficient power with the right cartridge or propellant according to the manufacturer’s specifications must be used.
4.2.2 Captive bolt stunners must be cleaned and maintained according to manufacturers specification.
4.2.3 Persons using captive bolt guns must be trained in safe handling and proper stunning placement.
4.2.4 A penetrative captive bolt must enter the brain to provide an effective stun.
4.2.5 If birds show signs of recovery after this type of stunning action must be taken to assess and resolve the reason.
4.3 Use of handheld electrical stunning devices and dry plate electric stunning
4.3.1 Handheld electrical stunning devices and electric plate stunners must provide a strong enough current and be in contact with the bird for long enough so that it is immediately unconscious.
4.3.2 Persons using hand held and plate electric stunners must be trained in safe handling and proper stunning placement based on the species being stunned.
4.3.3 Hand held and plate electric stunning equipment must only be used on the species that the manufacturer recommends and which it is designed for.
4.3.4 Birds must not receive pre-stun shocks
4.3.5 Recommended Electrodes should be placed to span the brain of the bird.
4.3.6 Recommended Stun settings and voltages should be recorded when hand held electric stunning or electric plate stunning is in use.
Note: guidance on appropriate current levels for different types of poultry can be found in Annex 1.
4.4 Use of electrical water stunning baths
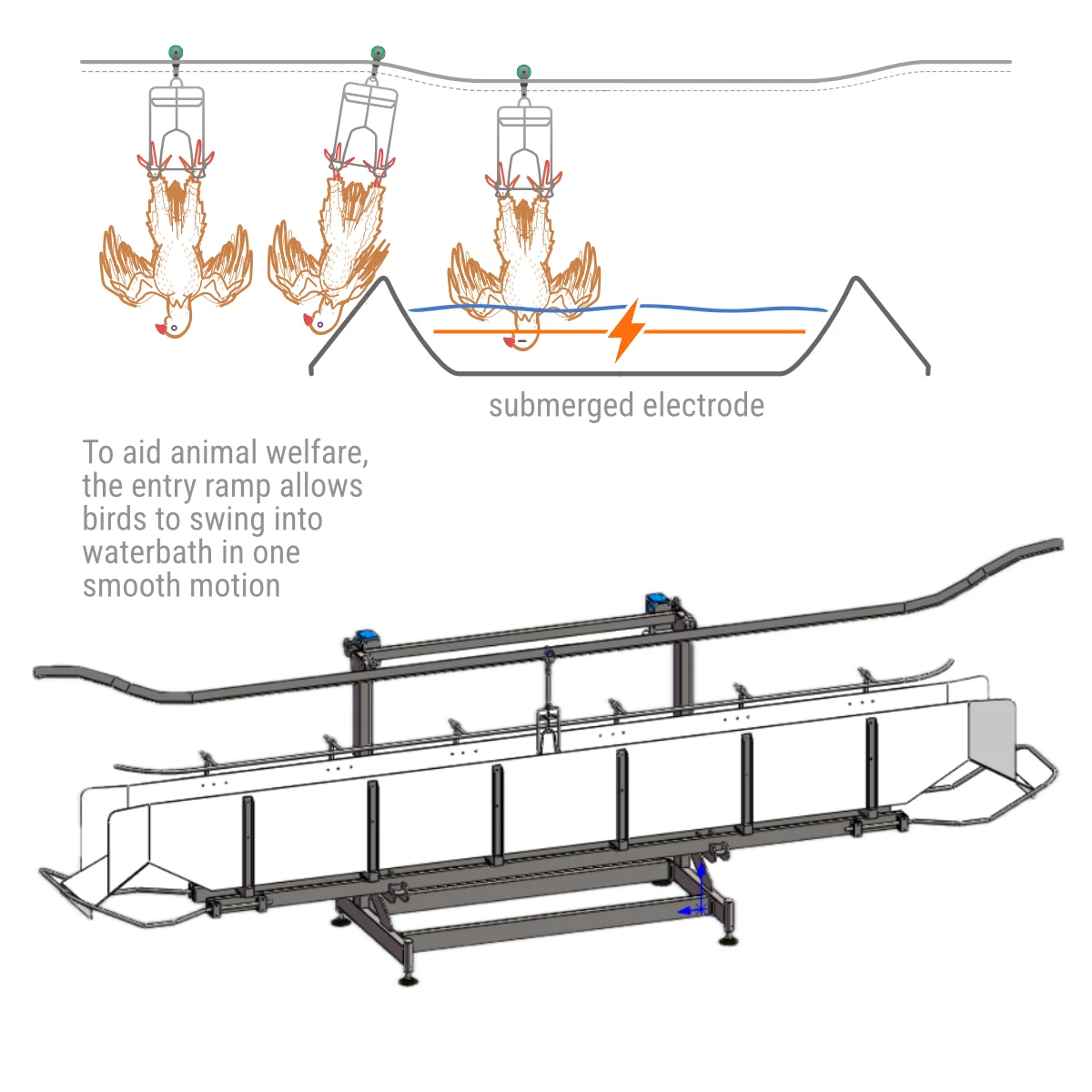
4.4.1 The strength and duration of the current used in electrical water baths must be such that the bird is immediately rendered unconscious and remains so until it is dead.
Note: guidance on appropriate current levels for different types of poultry can be found in Annex 1.
4.4.2 When an electrical water stunning bath is used, the water-level must be set at a height appropriate for the size and number of birds.
4.4.3 When an electrical water stunning bath is used the bath must be set such that the heads of all birds make effective contact with the water bath.
4.4.4 The water bath must be of sufficient size and depth and the water must not overflow at the entrance.
4.4.5 The electrode immersed in the water must extend the length of the water bath.
4.4.6 The water bath stunner must be designed and set up to prevent birds receiving pre-stun shocks.
4.4.7 Where poultry in a continuous flow in a shackle system are stunned in a water bath, the voltage and current used must be sufficient to produce a current strong enough to ensure that every bird is stunned.
4.4.8 The current must pass efficiently through the bird. In particular there must be good electrical contacts and the shackle-to-leg contact is kept wet.
4.4.9 There must be someone monitoring birds exiting the water bath stunner to check whether it has been effective in stunning the birds and who, where it has not been effective, will either stun and slaughter or kill any bird without delay.
4.4.10 Recommended water baths should be fitted with an ammeter to accurately monitor current flow through the bath when loaded with birds.
4.5 Use of Controlled Atmosphere Stunning (CAS) and Controlled Atmosphere Killing (CAK)
4.5.1 Recommended Controlled Atmosphere Stunning (CAS) and Controlled Atmosphere Killing (CAK) systems should be used to render poultry insensible.
4.5.2 Recommended The use of anoxic gases rather than CO2 is recommended for both CAS and CAK.
4.5.3 The controlled atmosphere system must rapidly cause insensibility.
4.5.4 Persons using the gas stunner must be trained in proper use of the stunning system.
4.5.5 Birds must be exposed to a carbon dioxide, nitrogen and/or argon gas mix at a concentration sufficient to cause unconsciousness and/or death quickly and calmly with the minimum of discomfort.
4.5.6 CAS/CAK using carbon dioxide must only be used in multi-phase processes (at least two phases) where birds are initially stunned by remaining in a mix of not more than 30% CO2 for at least a minute before moving into higher concentrations of this gas.
4.5.7 The gas system must be used according to manufacturer’s instructions.
4.5.8 In CAK systems birds must not be found to recover consciousness after exposure to the gas mixture.
4.5.9 Gas concentration in the chamber must be monitored.
4.5.10 Recommended Visible and audible warning signals should be displayed if gas concentrations fall below levels capable of producing an effective stun and/or kill.
4.5.11 Birds must not enter the system if gas levels are known to be too low to produce an effective stun.
4.5.12 There must be a means of monitoring birds which are in the chamber.
4.5.13 A competent person must be in attendance at all times when birds are in the chamber.
4.5.14 There must be a means of flushing the chamber with atmospheric air with the minimum delay.
4.5.15 There must be means of access to any bird in any part of the chamber with the minimum of delay.
4.5.16 Recommended Plants should record and investigate signs of damage or injury to the birds which has occurred while they are in the chamber.
4.6 Bleeding
4.6.1 Birds must be bled within 10 seconds of stun.
Note: This standard does not apply to birds from CAK systems.
4.6.2 When one person is responsible for both stunning and bleeding these operations must be carried out consecutively on each individual bird before moving on to the next.
4.6.3 The bleed wound must be large and allow rapid bleeding.
Note: The carotids or arteries from which they originate from must be severed, depending upon the species. The objective is to stop supply of oxygenated blood to the brain.
4.6.4 The bird must be observed during bleeding for signs of sensibility and if any are seen it must be re-stunned immediately.
4.6.5 Where automatic neck cutters are operated there must always be someone present to check whether or not the neck cutters have effectively severed at least one of the carotid arteries or the vessels from which they arise and to take action if they have not.
4.6.6 Birds must be checked to ensure they have been effectively slaughtered before entering a scald tank or plucking machine.
4.6.7 Birds must not be scalded or plucked until at least 90 seconds (for chickens) or 120 seconds (for turkeys, geese and ducks) have elapsed from the time of bleed.
5.0 STAFF AND TRAINING
5.0.1 There must be a named individual responsible for bird welfare within the facility that has the authority to take action should any welfare issues arise.
5.0.2 Training in humane methods of poultry handling must be made available to all staff working with live birds.
5.0.3 Staff must be trained to recognise signs of effective and ineffective stunning and signs of recovery of consciousness.
5.0.4 There must be clearly written standard operating procedures for every step of the operation and staff responsible for animal handling, stunning and slaughter must be familiar with these procedures.
ANNEX 1
| For stunning different types of poultry | <200 Hz | 200-400 Hz | >400 Hz |
| Chickens | 100mA | 150mA | 200mA |
| Ducks & Geese | 130mA | N/A | N/A |
| Turkeys | 250mA | 400mA | 400mA |
Guidance on appropriate current at different frequencies of the electrical stun system

The Certified Animal Welfare Approved by AGW (AWA) programme and food label promote the well-being of animals and the sustainability of farms and abattoirs. Their label adds value to meat products for those people who are raising and handling animals by connecting conscientious consumers with farmers and meat processors using high-welfare practices.
Certified Animal Welfare Approved by AGW has among the most rigorous standards for farm animal welfare currently in use in Africa, Europe and North America. Our standards are developed in collaboration with scientists, veterinarians, researchers and farmers across the globe to maximise practicable, high-welfare farm management.



